Warehouse Solutions
Complete Warehouse Labeling Best Practices Guide & Checklist
Why Labeling Matters
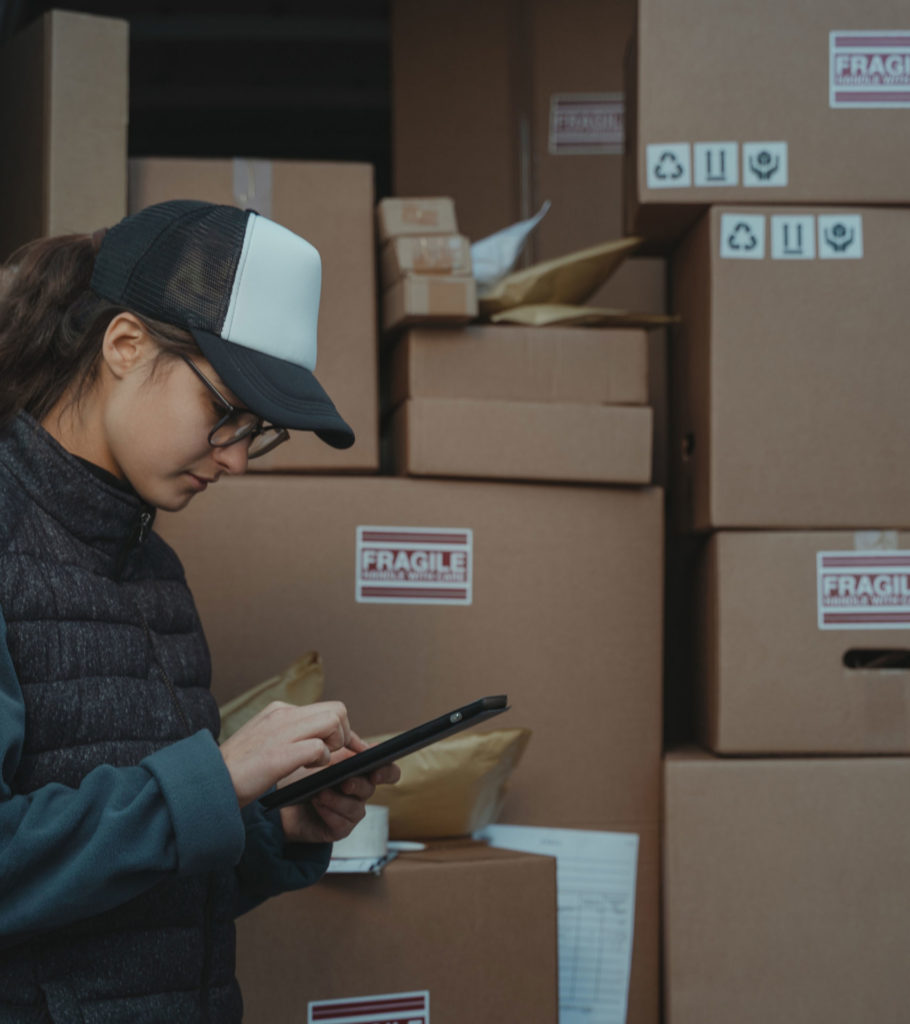
In a busy warehouse, clear labels act like a roadmap. When every aisle, shelf, and bin is marked, people find items faster and make fewer mistakes. Labeling is not just “stickers on shelves.” It builds a calm, organized system that boosts speed, safety, and accuracy. In this guide, you’ll see why labeling matters, which labels to use, how to roll out a system, and what practices keep it working.
The Business Impact
Labels guide storage and picking, so teams spend less time searching. As a result, orders ship faster and accuracy improves. Good labeling also supports safety rules and audit-ready compliance.
What Goes Wrong Without Labels
Without a system, items go missing, pickers guess, and errors multiply. That hurts customer satisfaction and your bottom line. It also raises safety risks when people store or handle items the wrong way.
Quick Wins from Better Labeling
Types of Warehouse Labels (and Where They Fit)
Core Categories
- Location labels: Identify aisles, bays, racks, and zones for fast navigation.
- Inventory labels: Show SKU, description, and quantity for quick checks.
- ID labels: Tag tools and equipment so teams can find and track them.
Data Carriers and Materials
- Barcode labels: Speed scans and cut manual entry errors.
- RFID tags: Enable real-time tracking and bulk reads across processes.
- Magnetic labels: Reposition locations in fast-changing layouts.
- Floor labels: Withstand traffic to guide paths and storage blocks.
- Hazard labels: Flag risks and handling steps to protect people.
- Quality labels: Mark pass/fail/hold states for QA visibility.
- Outdoor-durable labels: Survive sun, rain, and temperature swings.
How to Plan and Implement a Labeling System
The Payoff: Benefits You Can Measure
Speed and Accuracy
Clear labels cut walking and searching. Scanners read codes quickly, so orders move faster with fewer exceptions.
Inventory Confidence
Because every move is scanned, counts stay current. You avoid stockouts, overstocking, and pick errors that drive returns.
Safety and Compliance
Labels mark hazards and handling steps. In turn, audits go smoother and incidents drop.
Smarter Space Use
When you mark storage areas well, you use racks and floors more efficiently. That often removes the need for extra space.
Best Practices That Keep Systems Working
Keep It Consistent
Use the same colors, fonts, sizes, and placements. Consistency reduces confusion and speeds training.
Inspect and Refresh
Set a schedule to replace worn or outdated labels. Quick fixes preserve scan quality and trust.
Lean on Technology
Pair labels with barcode scanners and, when useful, RFID. This improves tracking and reduces manual touches.
Make It Visible
Place labels at eye level when possible. Use high contrast so teams can read them from the aisle.
Use Color with Care
Color coding helps teams sort areas, product families, or priorities. However, keep palettes small and readable.
Train and Retrain
Teach new hires the scheme on day one. Then refresh skills as layouts or rules change.
Design for Change
Build a system that adapts. Magnetic locations, modular signage, and scalable codes help you evolve without chaos.
Close the Loop
Ask floor teams what works and what fails. Then update standards based on real feedback.
Optimize for Scans
Protect quiet zones, use proper x-dimensions, and test with your actual scanners and angles.
Prioritize Safety Labels
Mark hazards and handling needs clearly. This protects people and supports compliance.
Final Thoughts
Warehouse labeling is not decoration; it is core infrastructure. When you plan it well, connect it to your WMS, and keep it current, you gain speed, accuracy, and safety. Above all, choose readable formats, train your team, and review often. Do that, and your labels will keep the operation running cleanly—today and as you grow.